Installing Passenger Enterprise + Nginx on an AWS production server
for Ruby apps + Ubuntu 17.10 (with APT)
On this page, we will install Passenger. After installing Passenger we can begin with deploying the app.
Table of contents
- Loading...
Heads up: limited package support for non-LTS Ubuntu versions
Before we continue, you should know that the Ubuntu version you selected is a non-LTS (Long Term Support) version. This means that Canonical — the company that created Ubuntu — only supports this particular Ubuntu version for 1 year.
Because of this short support cycle by Canonical, we only provide Passenger package updates for this Ubuntu version for 6 months. That's when the next Ubuntu version comes out.
So when the next Ubuntu version is released, you must upgrade your system to that new Ubuntu version. Otherwise you won't receive Passenger updates in the form of .deb packages from us anymore.
If you don't like having to upgrade your Ubuntu system every 6 months, then you should use an LTS version of Ubuntu. Canonical supports LTS versions for 5 years, and we provide Passenger package updates for LTS versions for 5 years too.
Now that you know this, let's move on.
Step 1: download and install your license key
Before you can install Passenger Enterprise, you need to download and install your license key. This is a regular file that you need to copy to your production server.
Please login to the Passenger Enterprise Customer Area.
Click on the Install button in the Customer Area.

Click on the button to download the license key.
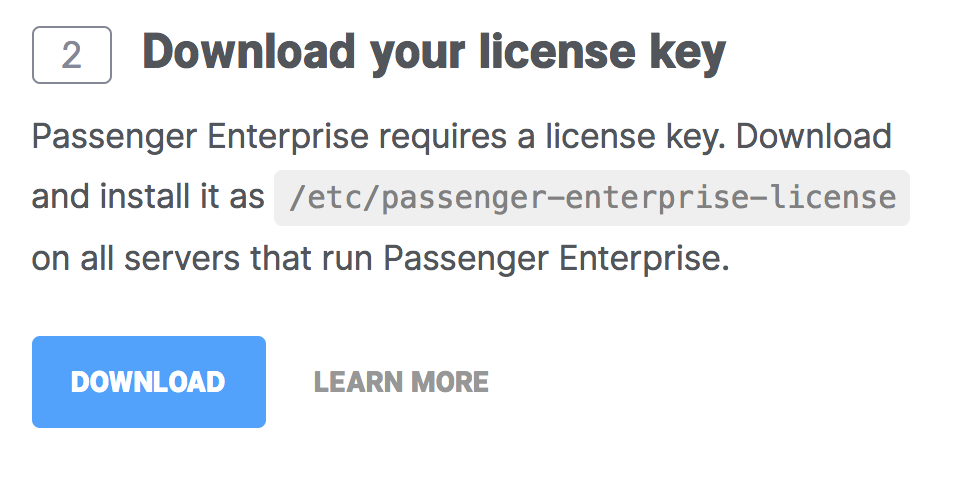
The license key will be downloaded to your local computer. Copy this license key file to your production server, for example using scp:
local-computer$ cd /path-to-your-local-computer-download-folder local-computer$ scp -i your_ec2_key.pem passenger-enterprise-license adminuser@yourserver.com:
Replace adminuser with the name of an account with administrator privileges or sudo privileges.
This is usually admin, ec2-user, root or ubuntu.
Finally, login to your production server and save the file as /etc/passenger-enterprise-license:
local-computer$ ssh -i your_ec2_key.pem adminuser@yourserver.com production-server$ sudo mv passenger-enterprise-license /etc/passenger-enterprise-license production-server$ chmod 644 /etc/passenger-enterprise-license
Step 2: obtain your download token
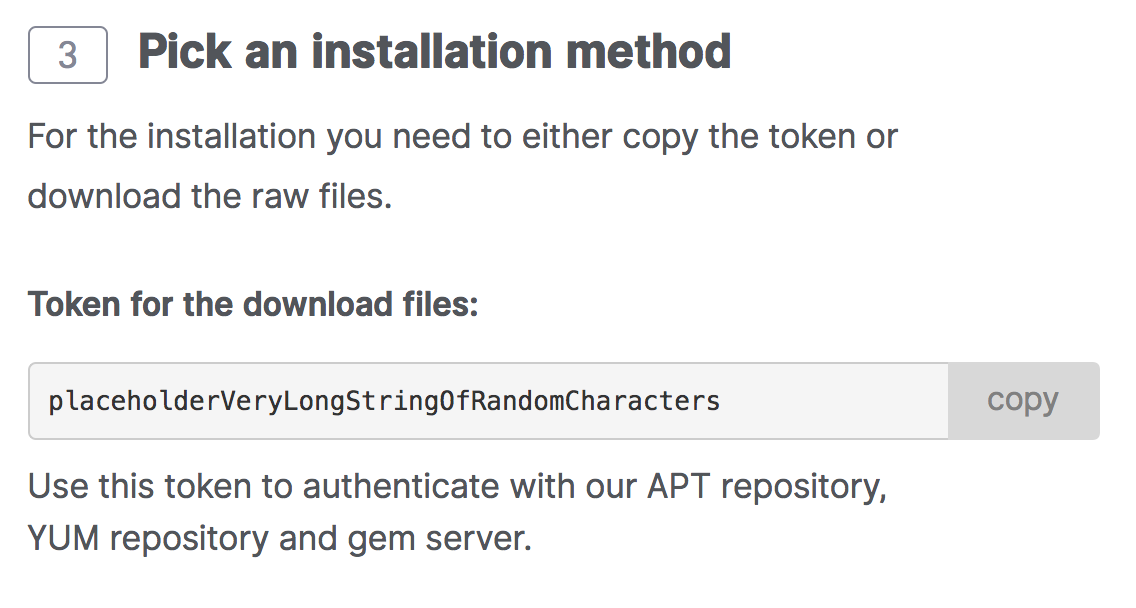
Your download token is needed in order to install Passenger Enterprise. In the Customer Area, find your download token and copy it to your clipboard.
Step 3: install Passenger packages
These commands will install Passenger Enterprise + Nginx module through Phusion's APT repository.
At this point we assume that you already have Nginx installed from your system repository. If not, you should do that first before continuing.
Replace YOUR_DOWNLOAD_TOKEN with the download token you obtained in the last step.
# Install our PGP key and add HTTPS support for APT
sudo apt-get install -y dirmngr gnupg
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys 561F9B9CAC40B2F7
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates
# Add our APT repository
unset HISTFILE
sudo sh -c 'echo machine www.phusionpassenger.com/enterprise_apt login download password YOUR_DOWNLOAD_TOKEN >> /etc/apt/auth.conf'
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://www.phusionpassenger.com/enterprise_apt artful main > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/passenger.list'
sudo chown root: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/passenger.list
sudo chmod 644 /etc/apt/sources.list.d/passenger.list
sudo chown root: /etc/apt/auth.conf
sudo chmod 600 /etc/apt/auth.conf
sudo apt-get update
# Install Passenger Enterprise + Nginx module
sudo apt-get install -y libnginx-mod-http-passenger-enterpriseStep 4: enable the Passenger Nginx module and restart Nginx
Ensure the config files are in-place:
$ if [ ! -f /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/50-mod-http-passenger.conf ]; then sudo ln -s /usr/share/nginx/modules-available/mod-http-passenger.load /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/50-mod-http-passenger.conf ; fi $ sudo ls /etc/nginx/conf.d/mod-http-passenger.conf
If you don't see a file at /etc/nginx/conf.d/mod-http-passenger.conf; then you need to create it yourself and set the passenger_ruby and passenger_root config options. For example:
passenger_root /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/phusion_passenger/locations.ini; passenger_ruby /usr/bin/passenger_free_ruby;
When you are finished with this step, restart Nginx:
$ sudo service nginx restart
Step 5: check installation
After installation, please validate the install by running sudo /usr/bin/passenger-config validate-install. For example:
$ sudo /usr/bin/passenger-config validate-install * Checking whether this Phusion Passenger install is in PATH... ✓ * Checking whether there are no other Phusion Passenger installations... ✓
All checks should pass. If any of the checks do not pass, please follow the suggestions on screen.
Finally, check whether Nginx has started the Passenger core processes. Run sudo /usr/sbin/passenger-memory-stats. You should see Nginx processes as well as Passenger processes. For example:
$ sudo /usr/sbin/passenger-memory-stats Version: 5.0.8 Date : 2015-05-28 08:46:20 +0200 ... ---------- Nginx processes ---------- PID PPID VMSize Private Name ------------------------------------- 12443 4814 60.8 MB 0.2 MB nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx 12538 12443 64.9 MB 5.0 MB nginx: worker process ### Processes: 3 ### Total private dirty RSS: 5.56 MB ----- Passenger processes ------ PID VMSize Private Name -------------------------------- 12517 83.2 MB 0.6 MB PassengerAgent watchdog 12520 266.0 MB 3.4 MB PassengerAgent server 12531 149.5 MB 1.4 MB PassengerAgent logger ...
If you do not see any Nginx processes or Passenger processes, then you probably have some kind of installation problem or configuration problem. Please refer to the troubleshooting guide.
Step 6: update regularly
Nginx updates, Passenger updates and system updates are delivered through the APT package manager regularly. You should run the following command regularly to keep them up to date:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get upgrade
You do not need to restart Nginx or Passenger after an update, and you also do not need to modify any configuration files after an update. That is all taken care of automatically for you by APT.
Next step
Now that you have installed Passenger, you are ready to deploy your Ruby application on the production server!